Reverse Linked List
Question
- leetcode: Reverse Linked List | LeetCode OJ
- lintcode: (35) Reverse Linked List
Reverse a linked list.
Example
For linked list 1->2->3, the reversed linked list is 3->2->1
Challenge
Reverse it in-place and in one-pass
题解1 - 非递归
联想到同样也可能需要翻转的数组,在数组中由于可以利用下标随机访问,翻转时使用下标即可完成。而在单向链表中,仅仅只知道头节点,而且只能单向往前走,故需另寻出路。分析由1->2->3变为3->2->1的过程,由于是单向链表,故只能由1开始遍历,1和2最开始的位置是1->2,最后变为2->1,故从这里开始寻找突破口,探讨如何交换1和2的节点。
temp = head->next;
head->next = prev;
prev = head;
head = temp;
要点在于维护两个指针变量prev和head, 翻转相邻两个节点之前保存下一节点的值,分析如下图所示:
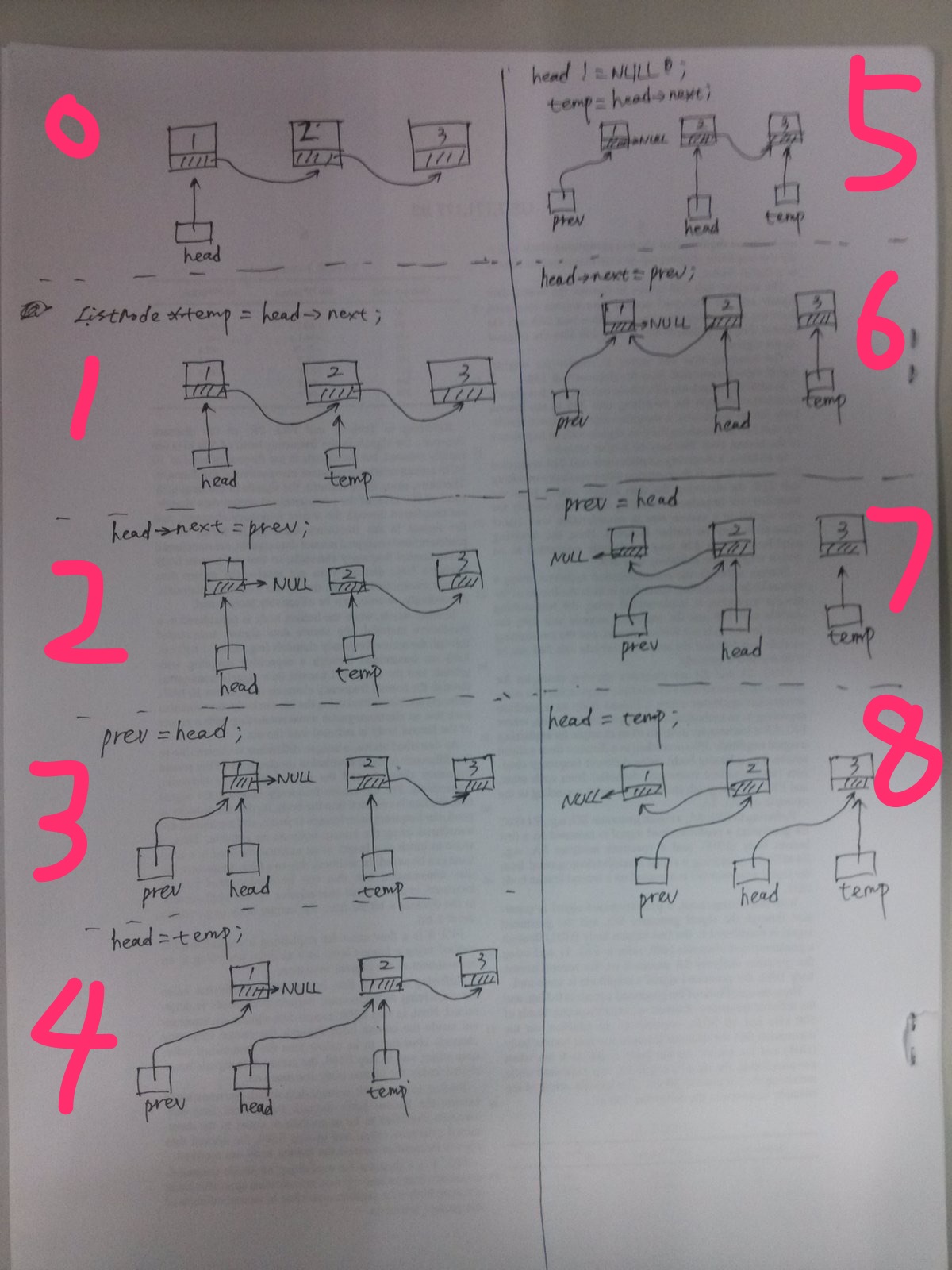
- 保存head下一节点
- 将head所指向的下一节点改为prev
- 将prev替换为head,波浪式前进
- 将第一步保存的下一节点替换为head,用于下一次循环
Python
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# @param {ListNode} head
# @return {ListNode}
def reverseList(self, head):
prev = None
curr = head
while curr is not None:
temp = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = temp
# fix head
head = prev
return head
C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *prev = NULL;
ListNode *curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
ListNode *temp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
}
// fix head
head = prev;
return head;
}
};
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode temp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
}
// fix head
head = prev;
return head;
}
}
源码分析
题解中基本分析完毕,代码中的prev赋值比较精炼,值得借鉴。
复杂度分析
遍历一次链表,时间复杂度为 , 使用了辅助变量,空间复杂度 .
题解2 - 递归
递归的终止步分三种情况讨论:
- 原链表为空,直接返回空链表即可。
- 原链表仅有一个元素,返回该元素。
- 原链表有两个以上元素,由于是单链表,故翻转需要自尾部向首部逆推。
由尾部向首部逆推时大致步骤为先翻转当前节点和下一节点,然后将当前节点指向的下一节点置空(否则会出现死循环和新生成的链表尾节点不指向空),如此递归到头节点为止。新链表的头节点在整个递归过程中一直没有变化,逐层向上返回。
Python
"""
Definition of ListNode
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
"""
class Solution:
"""
@param head: The first node of the linked list.
@return: You should return the head of the reversed linked list.
Reverse it in-place.
"""
def reverse(self, head):
# case1: empty list
if head is None:
return head
# case2: only one element list
if head.next is None:
return head
# case3: reverse from the rest after head
newHead = self.reverse(head.next)
# reverse between head and head->next
head.next.next = head
# unlink list from the rest
head.next = None
return newHead
C++
/**
* Definition of ListNode
*
* class ListNode {
* public:
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
*
* ListNode(int val) {
* this->val = val;
* this->next = NULL;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param head: The first node of linked list.
* @return: The new head of reversed linked list.
*/
ListNode *reverse(ListNode *head) {
// case1: empty list
if (head == NULL) return head;
// case2: only one element list
if (head->next == NULL) return head;
// case3: reverse from the rest after head
ListNode *newHead = reverse(head->next);
// reverse between head and head->next
head->next->next = head;
// unlink list from the rest
head->next = NULL;
return newHead;
}
};
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
// case1: empty list
if (head == null) return head;
// case2: only one element list
if (head.next == null) return head;
// case3: reverse from the rest after head
ListNode newHead = reverse(head.next);
// reverse between head and head->next
head.next.next = head;
// unlink list from the rest
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}
源码分析
case1 和 case2 可以合在一起考虑,case3 返回的为新链表的头节点,整个递归过程中保持不变。
复杂度分析
递归嵌套层数为 , 时间复杂度为 , 空间(不含栈空间)复杂度为 .
